Tungsten
We will explain main feature and physical properties of tungsten
Basic physical properties of tungsten.

Tungsten Ore
(1)Feature
- ・High melting point: Highest among all metals
- ・Heavy: Very high in density
- ・Hard. Very high in tensile strength
- ・Heat resistant. Excellent high temperature strength.
Lowest thermal expansion coefficient - ・Radiation shielding
- ・Least corrosion. Acid and chemical proof
(2)Physical characteristics
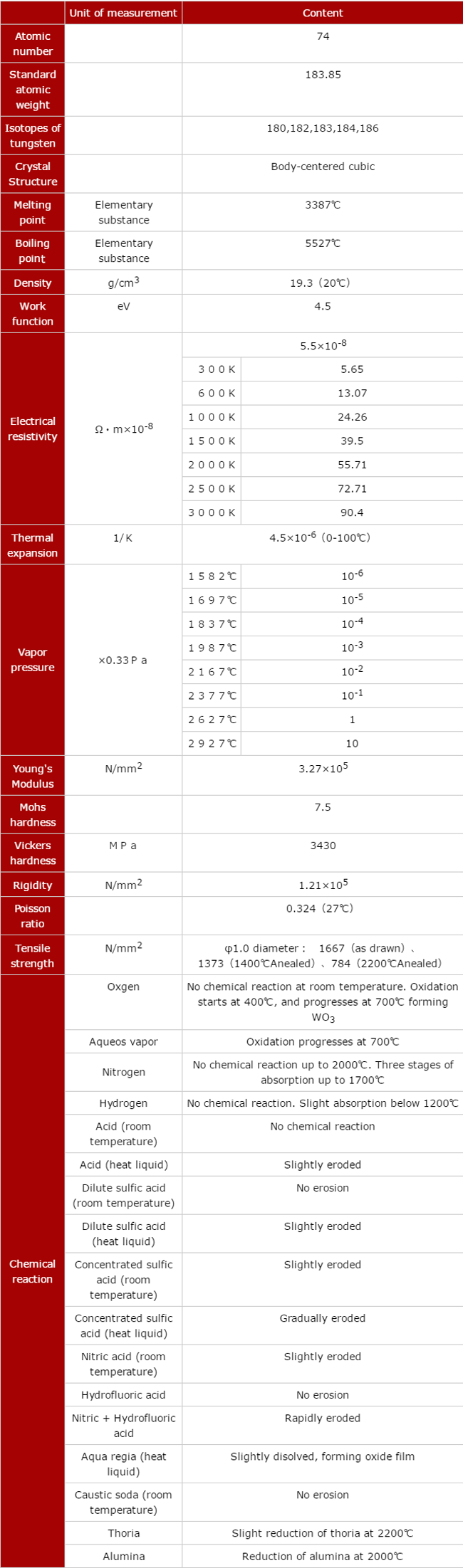
| Unit of measurement | Content | |
| Atomic number | 74 | |
| Standard atomic weight | 183.85 | |
| Isotopes of tungsten | 180,182,183,184,186 | |
| Crystal Structure | Body-centered cubic | |
| Melting point | Elementary substance | 3387℃ |
| Boiling point | Elementary substance | 5527℃ |
| Density | g/cm3 | 19.3(20℃) |
| Work function | eV | 4.5 |
| Electrical resistivity | Ω・m×10-8 | 5.5×10-8 |
| 300K 5.65 | ||
| 600K 13.07 | ||
| 1000K 24.26 | ||
| 1500K 39.5 | ||
| 2000K 55.71 | ||
| 2500K 72.71 | ||
| 3000K 90.4 | ||
| Thermal expansion | 1/K | 4.5×10-6(0-100℃) |
| Vapor pressure | ×0.33Pa | 1582℃ 10-6 |
| 1697℃ 10-5 | ||
| 1837℃ 10-4 | ||
| 1987℃ 10-3 | ||
| 2167℃ 10-2 | ||
| 2377℃ 10-1 | ||
| 2627℃ 1 | ||
| 2927℃ 10 | ||
| Young's Modulus | N/mm2 | 3.27×105 |
| Mohs hardness | 7.5 | |
| Vickers hardness | MPa | 3430 |
| Rigidity | N/mm2 | 1.21×105 |
| Poisson ratio | 0.324(27℃) | |
| Tensile strength | N/mm2 | φ1.0 diameter: 1667(as drawn)、1373(1400℃Anealed)、784(2200℃Anealed) |
| Chemical reaction | Oxgen | No chemical reaction at room temperature. Oxidation starts at 400℃, and progresses at 700℃ forming WO3 |
| Aqueos vapor | Oxidation progresses at 700℃ | |
| Nitrogen | No chemical reaction up to 2000℃. Three stages of absorption up to 1700℃ | |
| Hydrogen | No chemical reaction. Slight absorption below 1200℃ | |
| Acid (room temperature) | No chemical reaction | |
| Acid (heat liquid) | Slightly eroded | |
| Dilute sulfic acid (room temperature) | No erosion | |
| Dilute sulfic acid (heat liquid) | Slightly eroded | |
| Concentrated sulfic acid (room temperature) | Slightly eroded | |
| Concentrated sulfic acid (heat liquid) | Gradually eroded | |
| Nitric acid (room temperature) | Slightly eroded | |
| Hydrofluoric acid | No erosion | |
| Nitric + Hydrofluoric acid | Rapidly eroded | |
| Aqua regia (heat liquid) | Slightly disolved, forming oxide film | |
| Caustic soda (room temperature) | No erosion | |
| Thoria | Slight reduction of thoria at 2200℃ | |
| Alumina | Reduction of alumina at 2000℃ |